Reed relay's role in IC testing
Reed Relays play an essential role in semiconductor testing due to their high reliability and precision. They consist of two metal reeds that are sealed in a glass tube and act as the switch contacts, controlled by voltage that drives the internal coil to generate magnetic force.
How are Reed Relays used in IC testing
In IC testing, reed relays are used to connect and disconnect various pins and components of the IC, allowing for various tests and measurements to be performed. For example, a reed relay might be used to connect a specific pin of the IC to an external measurement device, such as an semiconductor testing system, Automatic Test Equipment (ATE), oscilloscope or multimeter, in order to measure the IC's function, RF performance, voltage or current.
Reed relays are especially useful in IC testing because they are very fast, have a low contact resistance, and can be controlled with high precision. Additionally, they can handle high frequencies and are relatively immune to interference from other signals in the testing environment.
To use a reed relay in IC testing, it is typically connected to a control circuit that can activate and deactivate the internal coil, causing the reed switch to close or open. This control circuit might be manually operated by an engineer or automated using specialized test equipment.
Overall, reed relays are a valuable tool in IC testing due to their reliability, precision, and speed, and are commonly used in a variety of applications in the semiconductor industry.
Bright Toward has served Taiwan’s semiconductor industry with small and reliable relays for over three decades. We have the experience and know-how to continuously develop better and more reliable relays to ensure our customers can successfully test ICs with increasingly complicated functions.
Why are Multi-channel Miniature Reed Relays useful in IC testing?
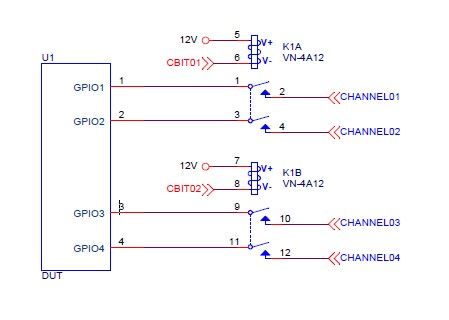
Multi-channel miniature reed relays are particularly useful in IC testing because they allow multiple connections to be made simultaneously and with high precision. Toward’s IC testing Reed Relays are packaged vertically for smaller surface size and designed with multi-channel up to 5 channels in a single package.
Here are a few reasons why multi-channel miniature reed relays are so useful in IC testing:
Reduced test Time
- With multiple channels, it's possible to perform multiple tests simultaneously, reducing the overall test time. This is especially important in high-volume production environments where time is a critical factor.
Space-saving
- Miniature reed relays take up very little space, allowing for more channels to be packed into a small area. This is particularly important in modern ICs, which can have hundreds or even thousands of pins in a very small area.
Precise control
- Miniature reed relays are very precise, allowing for high-precision control of the connection and disconnection of specific pins on the IC. This is important for making accurate measurements and for ensuring that the correct connections are made during testing.
Reliability
- Reed relays have a long operational life and can be cycled millions of times without failure. This is particularly important in IC testing, where reliability is critical to ensure that the testing process is accurate and repeatable.
More generally, the use of multi-channel miniature reed relays in IC testing can significantly improve the efficiency and accuracy of the testing process, leading to improved product quality and faster time-to-market.
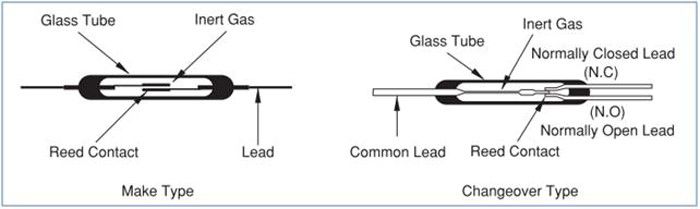
Diagram of the structure of a reed relay
As the below drawing shows, two leads with a reed contact are packaged in a glass tube. Inert gas is injected into the glass tube to minimize contact wear and increase reliability. We then sputter chemicals like rhodium, ruthenium, and iridium onto the contact for better reliability and stable contact resistance. The glass tube with reed contacts is then inserted into a coil and packaged into a reed relay.
Standard contact configurations include Form A (normally open when not driven), Form B (normally closed when not driven), and form C (normally open + normally closed). Please see the link in Related FAQ for contact configuration explanations. With the increasing number of testing sites on load boards and probe cards, two form A, four form A, and two form C are often packaged into a single reed relay to satisfy testing needs.
For example, Bright Toward provides a VN-4A reed relay comprising four individual channels with the internal reed switches vertically packaged to conserve PCB real estate, widely applied to APIC (Application Processing IC) and PMIC (Power Management IC) testing, where size and reliability and critical characteristics.
Why are Reed Relays’ On-Resistance Value important in IC Testing?
The on-resistance of a reed relay is an important parameter to consider in IC testing because it directly affects the accuracy and precision of the measurements being taken. The on-resistance is the resistance of the switch when it is in the closed position, and it can vary depending on the specific relay and its design.
Toward’s Reed Relays are developed to have low and stable contact resistance.
Here are a few reasons why the on-resistance of a reed relay is important in IC testing:
Accuracy
- The on-resistance of the relay can directly affect the accuracy of the measurement being taken. When measuring a voltage or current signal, for example, the on-resistance can add an additional resistance value to the measurement, leading to inaccuracies in the data. By using a relay with a low on-resistance, the impact of the relay on the measurement can be minimized.
Precision
- The on-resistance can also affect the precision of the measurement. When taking measurements at a small scale, even small changes in resistance can lead to significant changes in the measurement values. By using a relay with a low on-resistance, the impact of the relay on the measurement can be minimized, leading to more precise data.
Signal Integrity
- The on-resistance can also impact the signal integrity of the measurement. When the on-resistance is high, it can cause signal loss or distortion, particularly when high frequency signals are being measured. By using a relay with a low on-resistance, the impact on the signal can be minimized, leading to more accurate and precise measurements.
Overall, the on-resistance of a reed relay is an important consideration in IC testing because it can directly impact the accuracy, precision, and signal integrity of the measurements being taken. By selecting Toward’s Reed Relay that has low on-resistance, the impact of the relay on the measurement can be minimized, leading to more accurate and reliable testing results.
- Related Products
-
10W/250V/1.5A Reed Relay
BFH-2A-*** Series
This reed relay can carry current at 1.5Amps with load voltage at 250V, it is designed in a 2 Form A contact arrangment. Nominal coil voltage is in choices...
Details Add to cart3W/200V/0.5A Reed Relay
BFH-2C-** Series
This reed relay can carry 1.5Amps of current while loading 200V of voltage. It is designed in a 2 Form C contact arrengment. Nominal coil voltage is in choices...
Details Add to cart10W/200V/1A Reed Relay
VN-1-****
This vertical miniature reed relay is unique in its standing design to save board space, widely popular in Taiwan’s semiconductor testing industry. With...
Details Add to cart10W/200V/1A Reed Relay
VN-2A-****
This is a 2 Form A vertical miniature reed relay unique in its standing design to save board space, widely popular in Taiwan’s semiconductor testing...
Details Add to cart10W/200V/1A Reed Relay
VN-4A-****
This is a vertical miniature reed relay unique in its standing design to save board space. It is designed in 4 Form A, normally opened contact arrangement....
Details Add to cart10W/200V/1A Reed Relay
SIP-1A-****
This Reed Relay comes in 1 Form A contact arrangment. With load voltage at 200VDC and carry current at 1 Amps, nominal coil voltage is in choices of 5V, 12V,...
Details Add to cart3W/150V/0.5A Reed Relay
VSIP-1A**-**
With a unique standing design, the VSIP series reed relay is specifically designed to conserve PCB real estate, with a mounting surface at 6.85mm*3.81mm....
Details Add to cart10W/200V/0.5A Reed Relay
OSIP-1A**-**
With a unique tilted design, this reed relay is ideal in conserving PCB real estate. Load voltage at 200VDC and carrying current at 0.5 Amp. Nominal Coil...
Details Add to cart3W/200V/0.5A Reed Relay
USIP-1A**-**
This load voltage 200VDC, carrying current at 0.5 Amp standing design reed relay, is unique in its class, with the reed switch placed tilted within the relay....
Details Add to cart10W/200V/1.5A Reed Relay
MSIP-1A**-*
This miniature reed relay features a 40% smaller footprint compared to standard SIP reed relays, making them the perfect fit for high-density test matrices....
Details Add to cart10W/200V/1.2A Reed Relay
MSIP-2A**-*
This miniature reed relay can load volatge ar 200V with carry current at 1.2Amps. It features a 40% smaller footprint compared to standard SIP reed relays,...
Details Add to cart6GHz, 3W/200V/0.2A Reed Relay
BU-1C-**
This High Frequency Reed Relay can switch signals up to 6.5GHz with breakdown voltage at 200VDC and carry current at 0.2 Amp. it is designed with a Form...
Details Add to cart6GHz, 3W/210V/1A Reed Relay
BU-1A**
This is a High Frequency Reed Relay that can switch signals up to 6.5GHz with a breakdown voltage at 210VDC and carry currents up at 1 Amp. it is designed...
Details Add to cart - Related FAQ